Hailtracker utilises realtime data to provide accurate hail size estimates
across all radars in Australia. There are a number of tools available to
analyse both live and historical hail tracks across the country. This guide
will provide some information on how to use aspects of the website. For any
further technical equiries, please contact [email protected] for
information.
Step One:
Select a radar domain either by using the menu on the top, or by selecting
the round radar icons on the map interface. Hail sizes are available for within a
160km radial square of each radar station – this is a physical limitation due to the
curvature of the Earth resulting in unrepresentative radar data for longer distances
away from the radar.
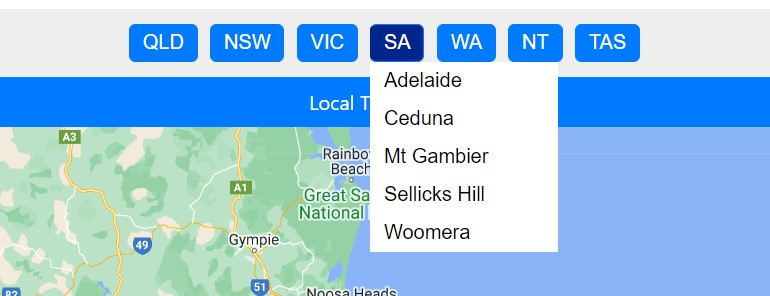
Above: Select the radar from the drop down list

Above: Enable/disable the radar icons on the map
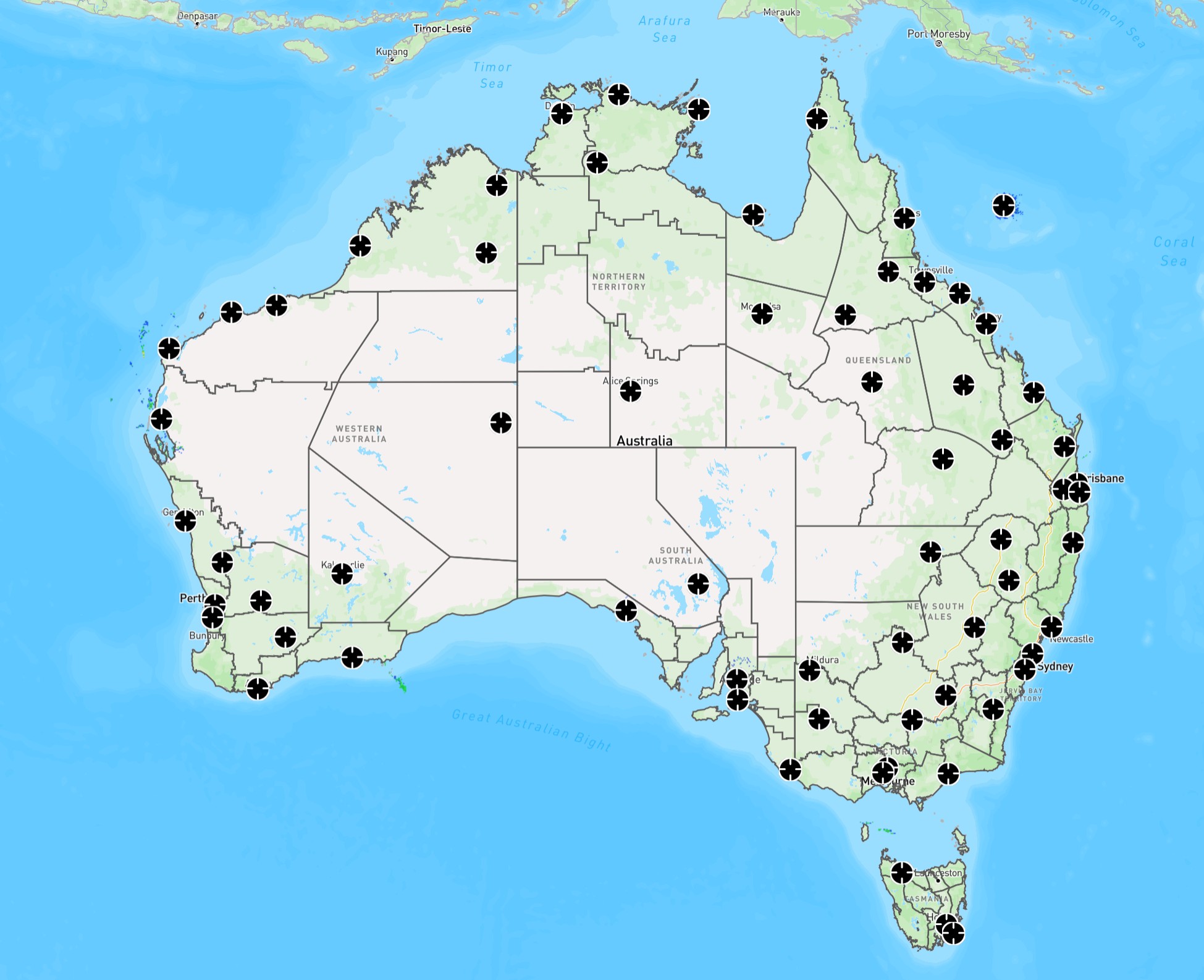
Above: Click on a radar icon to switch to that radar
The main landing page consists of a toolbar on the left side, locaiton selection
along the top, Google Map interface and scale underneath it.
Step Two:
Select the date from the 'Loop Controls' dropdown menu on the left. Currently you can only display
one date at a time. Dates are listed as year, month, day and presented in the local
time of the radar. Pressing 'Today' will default to today's date.
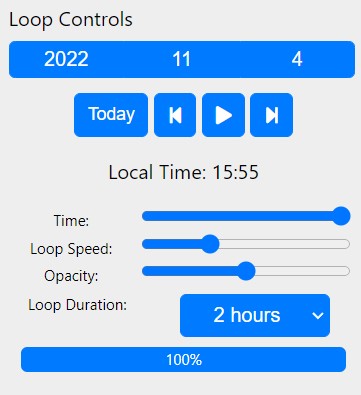
Above: Select the date from the dropdown menu
Step Three:
Select “Hail Sizes” from the 'Layer Type' menu. This is the default and most accurate layer
for analysing hail sizes and tracks. Radar (DBZ) will show the rainfall rates that you might
traditionally associate with a radar (blue = light rain, red = heavy rain/potential hail).
'MH 2019 75%'' may provide more accurate hail sizes under specific atmospheric conditions (generally
a cooler atmosphere) but will often overestimate the size of hail. 'Hail Wind Offset' will be explained
in Step 5.
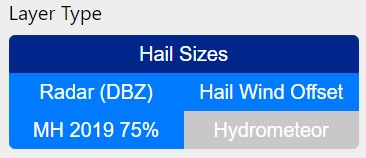
Above: Select 'Hail Sizes' for the best results
Step Four:
You have the option to view radar frames for each single time step (single), or view an entire hail
path (swathe). These are selected at the top under 'Display Time Range'. Swathe is the most useful view
to determine hail paths, however single views are useful to determine the time hail occurred (if required).
Note: Swathes are calculated from midnight to midnight UTC so the position of the time slider will determine
which date the swathe represents (A warning will be present if it is showing the previous day).
Above: Select swathe to view an entire hail track or single for individual frames
Step Four:
Step Five (Optional): The Weatherwatch HailTracker uses 3D radar technology to determine the maximum estimated
size of hail currently suspended in thunderstorms. On occasions, hail may melt (particularly on hot days, or
\if the hail is small) as it reaches the ground. In addition, there are times when wind in thunderstorms may
blow hail away from the updraft. We recommend the use of the “Hail Wind Offset” function for additional
verification. This overlays hail sizes in a contour, with the base radar reflectivity scan. If these two
are well aligned, it is unlikely hail has been blown away from the updraft, however if these two are not
aligned, the higher intensity echoes will display other locations hail may have fallen due to winds. To
use this feature, 'Radar (DBZ)' must be selected from the 'Layer Type' menu and then 'Hail Wind Offset'
can be simultaneously selected. The 'Swathe' view should then be selected from the 'Display Time Range' menu.
Above: Select 'Radar (DBZ)', 'Hail Wind Offset' and 'Swathe
The map can then be zoomed in to show how far the hail likely moved while falling to the ground. The
below image is an example taken from October 27, 2022 over the southern Gold Coast. Here the yellow and
red contours represent 2cm and 4cm hail tracks respecitvely, with the red/purple colours representing the
intenisty of rainfall/hail taken from just above the surface. As this storm moved towards the coastline,
the hail was recorded moving southwards and likely fell more over Tweed Heads than at Bilinga/Kirra.
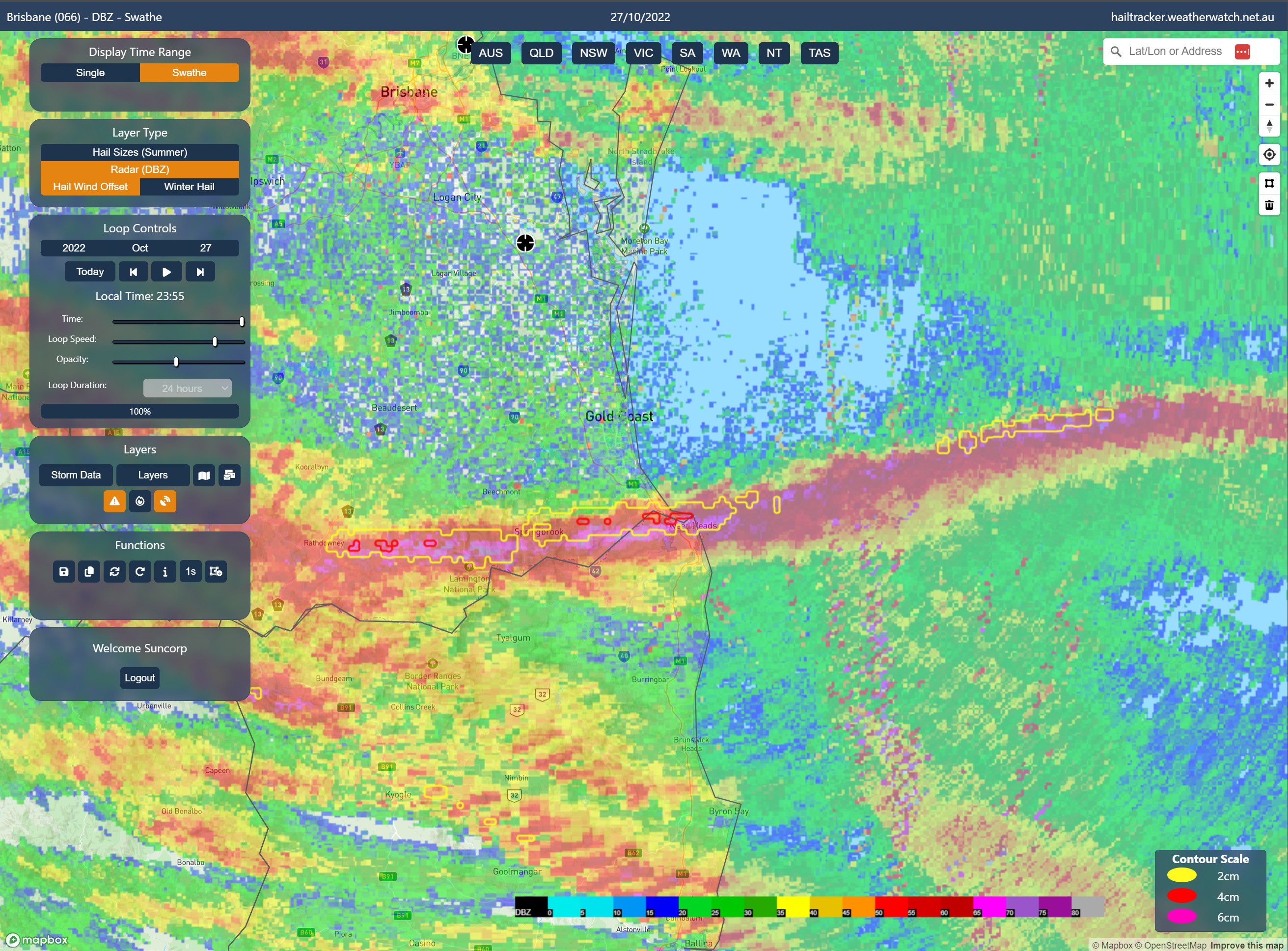
Above: Hail likely impacting the surface just south of where it was detected in the cloud...
FAQ:
There is no data available – can I order more data?
If you're interested in looking at historical data that is not available on the site, please contact
[email protected] and we can arrange this for you.
How do I know which radar I need?
There is a 160km radius from each radar where hail calculations are made. There is a search box in the top right
where an address can be typed in if looking for a specific property or area. Enabling the radar overlays (Step 1) will
help show what the closest radar to a particular location is.
HailTracker says a specific location has not been impacted, but nearby locations have been impacted – is
it still possible that large hail occurred?
HailTracker identifies hail as it develops high in the cloud. Storm days with strong shear can see this hail move as it
falls to the ground. The 'Hail Wind Offset' button (outlined in Step 5) will help determine if this hail has moved
from it's path.
Can I watch HailTracker live?
HailTracker is updated in realtime and you can watch hail swathes and single images update live. Select the 'Today'
button under loop controls will always ensure you have the most up to date view from the radar you are currently
looking at. You can also turn on the auto-refresh or manually refresh the display to get the latest frames.
Why does the swathe view show no hail?
Swathes are calculated from midnight to midnight UTC and therefore will not always align correctly with the
local radar time. A warning will display under the swathe button if you are going to view the previous days swathe.
If this warning is showing, move the time slider to later in the day to view the next swathe.








